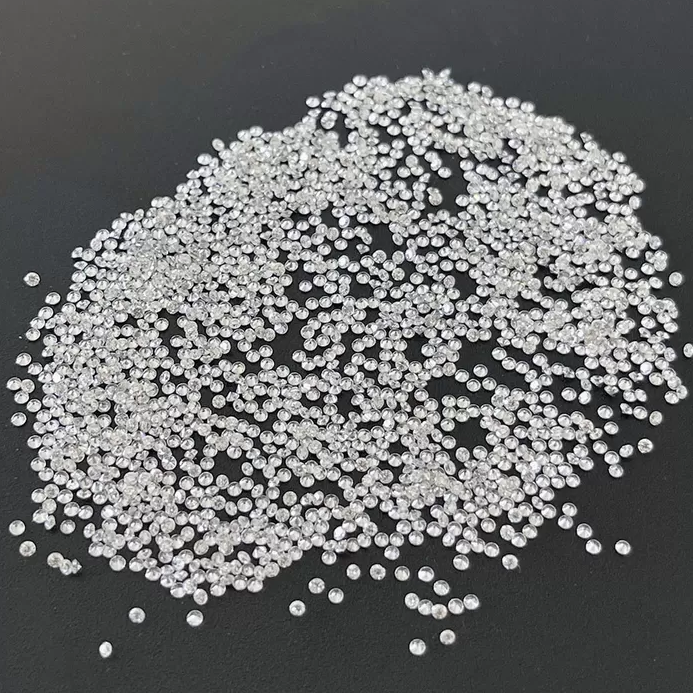
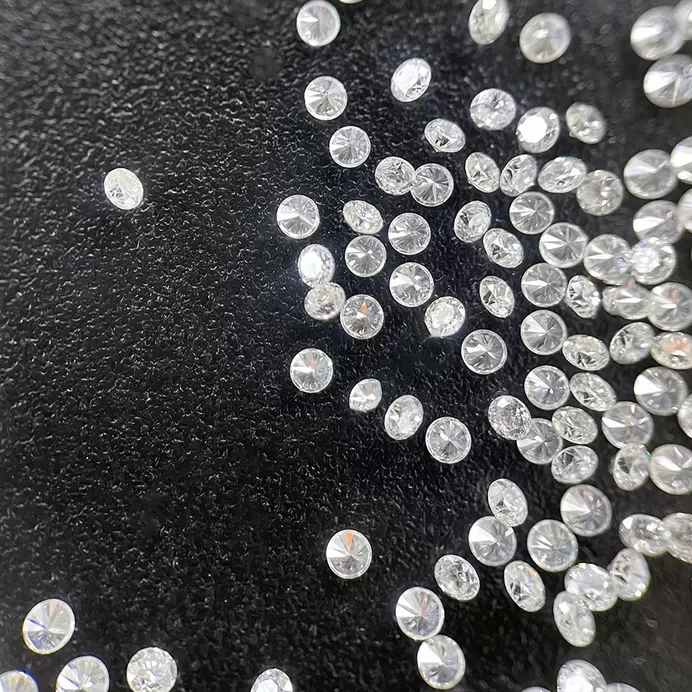
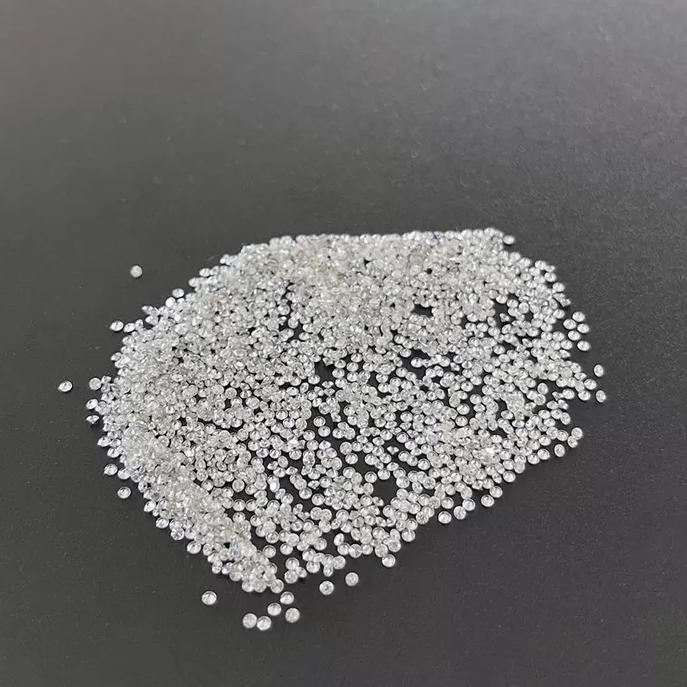
GH VS SI 0.01ct 0.02ct Synthetic Melee Diamonds For Earrings
GH VS SI 0.01ct 0.02ct Synthetic Melee Diamonds For Diamond Earrings
Synthetic Melee Diamonds Description
Diamonds are famous all over the world as luxury and precious jewelry. However, it is also the hardest substance in nature, a good heat conductor and an inert substance. These characteristics mean that diamonds can play an important role in some industrial applications, such as metal cutting, drilling, grinding, mining and construction, as well as applications in high-pressure testing and high-performance bearings.
Lab grown diamonds is usually produced by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or high pressure high temperature (HPHT).
Perhaps the oldest way to make diamonds is through a high-pressure, high-temperature process. Since the mid-1950s, laboratory diamonds have become part of the market through this technology.
General Electric first introduced this method, which follows the natural process of diamond creation. It imitates the process of making natural diamonds. It involves using pressure and heat to crystallize carbon deep in the earth.
Laboratory grown diamonds can also come from the CVD process. CVD represents chemical vapor deposition.
CVD diamonds come from various gases, such as methane. They are stored in a vacuum chamber, which decomposes the molecules of the gas, and then these molecules gather on the pre-existing diamond seeds.
Synthetic Melee Diamonds
What are Synthetic Melee Diamonds? This article will discuss the characteristics, costs, and sources of these lab-created diamonds. In addition, we’ll talk about the HPHT process that produces hundreds of thousands of carats per month. This method is not the only choice when looking for a diamond. It’s also the safest way to produce diamonds without damaging the environment. But beware: It’s also the most expensive.
Lab-created diamonds
If you are planning to purchase a piece of jewelry, you should know about the difference between natural and lab-created synthetic Melee diamonds. Melee diamonds are smaller than round diamonds, but they’re still quite valuable. Due to their unique design, they can give a great shine. Jewelry collectors love this type of stone for its value and aesthetic appeal. They’re most commonly used in rings and other jewelry pieces.
The process of making melee lab diamonds is the same as for other lab-grown diamonds. It involves placing a sliver of a natural diamond into a vacuum chamber, exposing it to hydrogen, methane, and microwave rays. The growth patterns of these synthetic diamonds are very distinctive to experts. For these reasons, it’s important to get a professional opinion before purchasing a diamond.
The process of making lab-created diamonds is relatively straightforward and conceptually straightforward. It was first developed in the 1970s and was used commercially in the 1990s. Russia and China are two of the biggest producers of lab-grown melee. Both countries produce over 200,000 carats a year. But there are still many questions about how this technology works. For now, the benefits outweigh the downsides.
The primary problem of contaminated melee diamonds is that they are cheaper than natural ones. This makes them an inferior option. However, some companies are producing these diamonds at lower prices than natural ones. Currently, the price of synthetic diamonds has been significantly lower than that of natural diamonds, and many manufacturers are targeting the global gem market. However, this situation is only temporary. In 2015, the pollution of melee diamonds with synthetics has become a major issue in the industry.
Characteristics of synthetic diamonds
A key characteristic of a synthetic diamond is its atypical PL spectrum. This characteristic makes it difficult to distinguish individual growth zones. Moreover, a synthetic diamond can show atypical growth patterns, which are probably caused by the growth using various faces of the seed crystal. While the size of a synthetic diamond is much smaller than its natural counterpart, it can still be easily identified using a DiamondView imaging tool.
Although most synthetic melees are formed from 100-carat seed crystals, some synthetic diamonds are created from 110-carat dodecahedra or 111-carat octahedra. These synthetic diamonds do not show a typical PL spectrum, although they exhibit sharp emission in the NV center. In addition, they show a slight presence of Si or H3. The gemstones may be considered synthetic because of their low price and low production costs, but despite their low price, the industry must pay attention to how these diamonds are produced.
In November, the demand for the low-end segment stabilized. While the average price of rough diamonds fell by about 15%, AWDC reported that their imports of diamonds to Belgium were up 34%. In addition, the diamond pipeline had accumulated considerable amounts of small-carat rough. This increase, however, came at the expense of a sharp adjustment in the prices of vulnerable goods. This could be a sign that the low-end diamond segment will eventually recover.
The price of large-size natural diamonds is approximately three times more expensive than their synthetic counterparts. Miners are trying to defend the legend of uniqueness by using sophisticated marketing and tracing programs to ensure that their stones are authentic. However, synthetic melee may soon become a differentiator for luxury retailers. However, the fact remains that synthetics are slowly taking over the industry. In fact, the production costs of natural melee have now surpassed the cost of the synthetics.
Cost of synthetic diamonds
Whether you’re considering a solitaire diamond engagement ring or a more affordable, low-cost stud earrings, a Melee Diamond is a great choice. These diamonds are small, ranging from 0.001 carats to 0.2 carats. Their high-quality shine makes them a good choice for jewelry collectors. The cost of synthetic Melee diamonds depends on their quality and the overall impact of the jewelry.
A reputable lab like the GIA has high-tech instruments and highly skilled professionals who can evaluate any inclusions. The most experienced scientists are trained to look closely at inclusions to determine if they are made of iron-nickel-cobalt, a material that is not found in natural diamonds. However, this method is expensive and time-consuming and not affordable to everyone. Because of this, many diamond sellers are opting to sell these diamonds in large parcels of hundreds of diamonds.
A melee diamond has two cuts: a single cut, which has only seventeen or eight facets, and a full cut, which has 57 or 58 facets. The former is used for halo and pave settings. Single cuts, on the other hand, are mostly used on watches. Generally, the cost of synthetic Melee diamonds is much less than full-sized diamonds.
Increasing competition and the availability of cheap, synthetic Melee diamonds may cause a divagation in the market for natural diamonds. As the synthetic market grows, however, the market for natural diamonds will merge, and mixed parcels of natural and synthetic diamonds will be the norm. Then, the question of price will be raised for both types of diamonds. And, if this happens, it’ll only be a matter of time before the natural and synthetic diamond markets merge and prices will become competitive.
Sources of synthetic diamonds
When it comes to diamonds, there are many types and colors to choose from. While many synthetic diamonds are made from carbon from volcanic ash, others are made from diamond dust or other minerals from the Earth’s crust. In fact, there are even synthetic diamonds made from human hair. The diamonds are available in a wide range of colors, starting in the $4000-$6000 range for a one-carat stone.
As a natural diamond, diamonds are formed deep in the earth, crystallizing under high pressures and temperatures. To create synthetic diamonds in the lab, scientists use two distinct processes. One is high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT), which replicates nature’s process of diamond formation. The other is chemical vapor deposition (CVD), which is the opposite of HPHT, and works by freeing carbon atoms, which then join together to form a diamond.
Despite their similarities, synthetic diamonds are much more affordable than their natural counterparts. Because they are artificial, they can trick some people into thinking they are natural diamonds. The quality of synthetic diamonds is constantly improving, and the Gemological Institute of America is looking into ways to distinguish between natural diamonds and synthetic diamonds. A recent study shows that they are more than 50% cheaper than their natural counterparts. There are also benefits for consumers as well.
HRTEM can be used to image the interface between diamond particles and growing graphite-like structures. The annealing temperature is varied to produce intermediates in the diamond-to-graphite transformation. As can be seen from Figures 7.2A and 7.11, the graphitic layers are curved. This results in a mosaic-like structure on the diamond core. The length of growing folds is between five and seven nm. Upon annealing, the surface of the particle may split apart, forming divergent tubular-like structures.
Detection of synthetic diamonds
There are some simple ways to detect synthetic melee diamonds. One of them is phosphorescence. This phenomenon is caused by the trace amounts of boron in HPHT diamonds. While phosphorescence is not present in natural diamonds, it does appear in HPHT diamonds. In fact, HPHT diamonds are so bright that they appear to glow for about 50 seconds when in the light.
To test for the presence of iron in synthetic melee diamonds, reputed Hi-Fi labs use advanced instruments. Experienced scientists can examine the inclusions in great detail. Using these instruments, the scientists can identify whether the stones are made of iron-nickel-cobalt, which is not found in natural diamonds. The problem is that not every individual has access to such expensive and time-consuming instruments.
Fortunately, the methods used to detect synthetic diamonds in melee size have improved dramatically in the last few years. While these methods can help identify some synthetic diamonds, they are not 100% accurate. The quality and experience of those operating the equipment, and the screening and analytical methodologies used can make a huge difference in the safety of the process. If the synthetic diamonds are able to be identified, the next step is to distinguish them from natural ones.
GSI has developed a highly effective method to identify synthetics in small diamonds. It uses high-throughput technology to identify diamonds that are not natural. The Surat office provides service to the world’s capital of small diamond manufacturing. A number of methods are used in the laboratory to determine whether synthetic diamonds are in a piece of jewelry. All these methods can be used to distinguish natural and synthetic diamonds in the jewelry manufacturing process.
GH VS SI 0.01ct 0.02ct Synthetic Melee Diamonds For Earrings