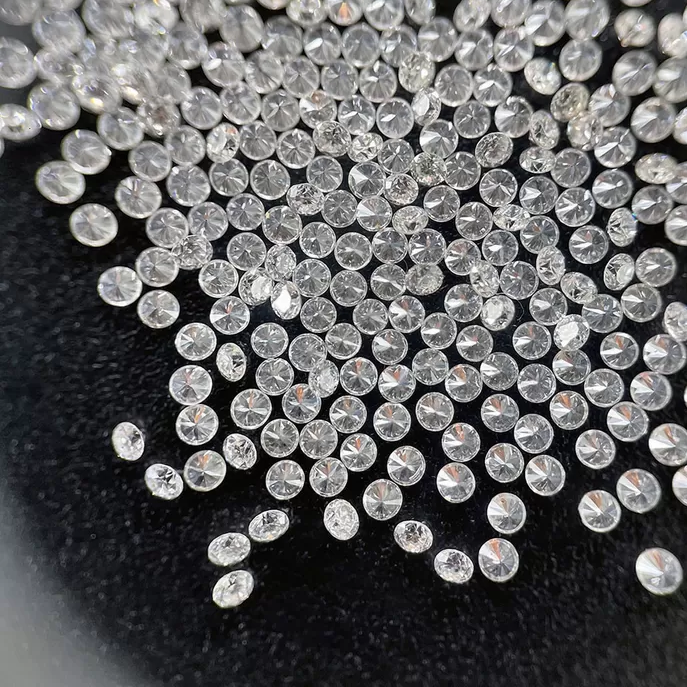
D E F Color 2mm 2.5mm Lab Grown Melee Diamonds OEM ODM
2mm 2.5mm D-E-F Color Lab Grown Melee Diamonds For Diamond Jewelry Making
Lab Grown Melee Diamonds Description
Lab-grown diamonds are diamonds grown in the laboratory using equipment that simulate the growth environment of natural diamonds. Both lab grown diamonds and natural diamonds are real diamonds. The main chemical components of lab grown diamonds and natural diamonds are carbon.
Lab grown diamonds is usually produced by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or high pressure high temperature (HPHT) methods.
HPHT synthetic diamonds usually contain metal co-solvent inclusions, which are black and opaque under transmitted light, and appear metallic under reflected light. This is because during the growth of HPHT diamonds, metals used as catalysts sometimes enter the diamond crystals. These co-solvent metal alloys contain elements such as iron, nickel, and cobalt.
CVD synthetic diamonds do not contain metal inclusions. But they usually contain dark graphite inclusions or other mineral inclusions, which are formed during their unique growth process. Graphite inclusions are different from metal inclusions in that they have no metallic luster. The CVD process is very different from the formation of natural diamonds. In a vacuum chamber filled with a hot mixture of hydrocarbon gas and hydrogen, extremely low pressure is applied, and diamonds are produced. Under normal circumstances, heating the mixture at such low pressures will produce graphite or some other non-diamond form of carbon. But in the CVD growth chamber, some of the hydrogen is converted into hydrogen atoms, which promotes the formation of diamonds, because diamonds are more stable in this environment. The conversion of hydrogen molecules into hydrogen atoms is accomplished by the application of microwaves, electric discharges or hot wires.
D E F Color 2mm 2.5mm Lab Grown Melee Diamonds OEM ODM
Tidbits about lab-grown diamonds
What Are Lab Grown Melee Diamonds?
The term “Lab Grown” is used to describe a new kind of diamond that is grown in a laboratory. Unlike natural diamonds, which are cut and polished, lab-grown diamonds have no rough or polish. The diamonds’ rough and polish are standardized by GIA and De Beers. As a result, their quality and grading is guaranteed. The full disclosure is delivered through specialized reports and laser inscriptions on the stone. These specialized reports have the potential to detect and identify mounted lab-grown melee diamonds.
GIA
GIA’s Melee Analysis Service helps distinguish between natural diamonds and lab-grown or treated diamonds. Using an automated system, GIA analyzes melee to separate fancy-shaped and round diamonds from simulants and treated or simulated stones. GIA seals each piece of melee in a secure packaging and ships it back to the client. Because of their small size, melee diamonds are often less expensive than their larger counterparts.
GIA Melee Diamonds are created in the same laboratory as other lab-grown diamonds, using the same processes. This process is known as chemical vapor deposition, and involves the use of a vacuum chamber and gases from the surrounding atmosphere. The material is then deposited onto the diamond by a combination of heat and plasma. GIA diamonds are considered conflict-free. This certification provides reassurance that you’re buying a diamond without the ethical question of its origin.
GIA’s amendments also protect consumers by ensuring that the GIA grading report has the same scale for both mined and lab-grown diamonds. This policy change will benefit both GIA and the companies selling lab-grown diamonds. The change will take effect in the fourth quarter of 2020 and will allow GIA to offer full color grading for lab-grown diamonds. GIA has long touted itself as a nonprofit educational institution that does not have a vested interest in any industry, but is now willing to adopt changes to serve the needs of the consumer.
Since 2008, GIA has been grading GIA-certified lab-grown diamonds. The GIA’s LGDR is an electronic-only detailed report with a QR code to access an educational website. GIA inscriptions on the girdle of the stone are unique to this process. These diamonds can be graded for color and clarity as a GIA-certified diamond.
De Beers
A De Beers spokesperson confirmed the company had been testing five pre-production prototype automated melee screening devices in Antwerp for two years. The automated devices will be packaged in a sealed IIDGR package, eliminating any concerns about disclosure. The new machines are capable of separating mined and lab-grown diamonds as small as one point. De Beers plans to roll out the automated screening machine in Antwerp next month.
While the price of mined diamonds has remained largely unchanged for the past 130 years, De Beers’ lab-grown diamonds are expected to be cheaper than naturally mined stones. The company will continue to price the synthetic stones lower than mined diamonds, so that they will not slash the industry’s profit margins. Millennials are driving the growth of the market for lab-grown diamonds, because they believe these stones are more environmentally friendly and conflict-free. The modernity of the process may also appeal to millennials.
While De Beers claims to control the market, this is largely untrue. China already dominates the melee market, and is ahead of De Beers’ 2020 production goals. By legitimizing these diamonds, De Beers is legitimizing a new category of smaller diamonds. There are already Chinese producers that are producing and selling diamonds cheaper than other suppliers. In addition, consumers will soon be able to buy De Beers diamonds for their wedding rings and engagement rings.
In addition to making these diamonds more affordable, lab-grown diamonds can also be used in industrial applications, such as in cutting tools and high-power electronics. As long as the quality of the diamond is high enough, it’s worth purchasing a De Beers lab-grown diamond. However, some critics say that lab-grown diamonds are not as valuable as their natural counterparts. The company has established a dedicated research center in the UK to develop more cutting-edge techniques and produce a higher-quality stone.
Whiteflash
What makes these diamonds different from their conventional counterparts? While melee diamonds are real, they are much smaller than traditional diamonds. Grading small diamond pieces is expensive and time-consuming, which would raise the price. Thus, these diamonds are generally sold in large parcels, with prices based on carat weight. Listed below are some of the characteristics of these melee diamonds.
A CUT ABOVE – This diamond is too small to receive laboratory certification, but it meets Whiteflash’s exacting standards. It also has an impressive inventory of natural diamonds. The A CUT ABOVE diamonds are cut to the highest standards and tested by the company’s team. Moreover, they are carefully selected by Whiteflash to meet their quality standards. In addition, Whiteflash diamonds are not available in fancy colors or moissanite.
MELETTE – A straight baguette is similar to a tapered baguette but is almost rectangular in shape. This diamond is ideal as an accent because it tends to appear larger than it really is. A trillion cut melee diamond is a triangular stone that draws attention to the main stone. This type of melee diamond is also very affordable. However, it is essential to compare melee diamond prices with the price of jewelry before making a purchase.
– Choosing a cut that reflects the individuality of the individual wearer: While whiteflash has developed a brand of premium-quality diamonds, it also has a social mission. Their A Cut Above diamonds are superior to 99% of other diamonds in the market. They cost between 10-15% more than a generic triple-excellent or AGS triple-ideal stone.
China
A panel at JCK Las Vegas said that the industry cannot expect lab-created diamond producers to fill that gap anytime soon. However, they did say that the natural diamond industry is currently having difficulty sourcing melee. The growth of CVD technology has made the production of larger stones more economical for growers. These diamonds are growing in popularity among consumers. And because the price of natural diamonds has fallen, many people are turning to synthetic diamonds to make their jewelry more beautiful.
The growth of lab-grown diamonds is being driven by China. According to Morgan Stanley, the country will account for up to 15% of global gem quality melee diamond production by 2020. In addition, the country will account for 7.5 percent of the global market for larger stones. However, some traditional sellers of natural diamonds are wary of the growing popularity of lab-grown diamonds. The reason for the growth of the market is that these stones are more competitive and attractive to younger, less-affluent consumers who are more conscious of the environmental impact of mining diamonds.
While this trend may not be sustainable, it is not impossible. Currently, China and India are two major producers of high-quality diamonds. China produces over 200,000 carats of lab-grown melee annually. And this growth rate is expected to continue as the two countries’ technology improves. The market for diamonds will increase, enabling Indian growers to capture a larger share of the global diamond market.
As with natural diamonds, laboratory-grown stones can have inclusions. While most of the stones are colourless, some are yellow or brown. Rarely, a diamond can be pink, red, or orange. Natural diamonds can come in any cut, but synthetic diamonds are usually cut as round brilliants. GIA began grading synthetic diamonds in 2006, and now has an independent lab for comparing the two.
Angola
There are many reasons to buy conflict-free, Lab Grown Melee Diamonds from an African mine. Conflict-free diamonds have been sourced without the involvement of human rights violators and have no environmental impact. Buying conflict-free diamonds can help stop the spread of civil war and contribute to the elimination of child labor and slavery. Because the diamonds are grown in labs instead of being mined, they are eco-friendly, ethical, and have no questionable origins.
The production of Lab Grown Melee Diamonds is similar to that of other lab-grown diamonds. The process, known as Chemical Vapor Deposition or HPHT, involves using a vacuum chamber and gaseous atmosphere to deposit material. As the gasses condense and combine, they form a diamond around the seed. This process produces diamonds with the same color, clarity, and carat weight as natural diamonds. Lab-Grown diamonds from Angola are less expensive than the ones from other countries, but the quality is a bit inferior.
In addition to GIA certifications, a lab-grown Melee Diamond can come with a certificate of authenticity from a reputable lab. When you buy an authentic Lab-Grown Melee Diamond from Angola, you can expect it to last a lifetime. However, it is essential to choose a high-quality diamond. The wrong kind of loose diamond can cause a safety hazard.
Swiss Gemmological Institute scientists recently developed an automated machine that can differentiate between natural-mined and lab-grown diamonds. This machine allows analysts to analyze large quantities of melee diamonds in a short time. The Swiss Gemmological Institute (SSEF) has also created an Automated Spectral Diamond Inspection machine. The ASDI machine is the first of its kind to be able to identify synthetic diamonds in bulk.
D E F Color 2mm 2.5mm Lab Grown Melee Diamonds OEM ODM