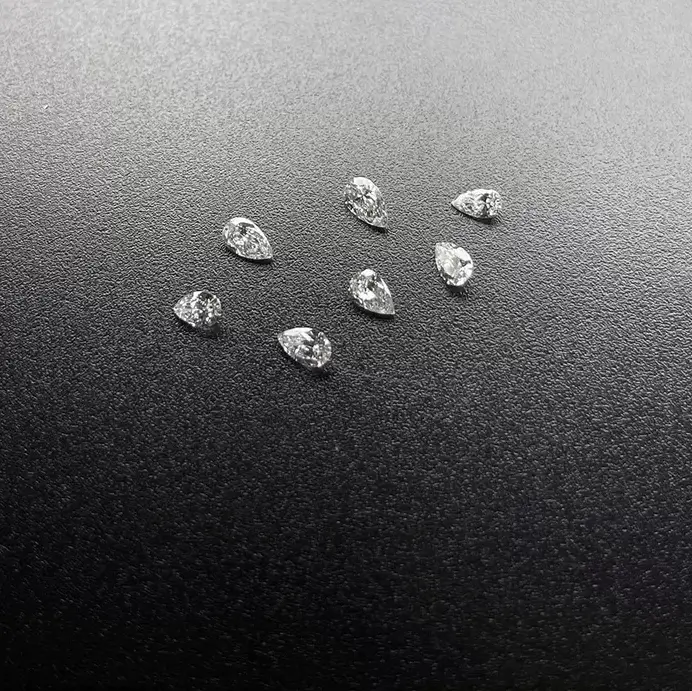
DEF Color HPHT Pear Shape Fancy Cut Lab Diamonds 0.05ct To 0.3ct
DEF Color HPHT Pear Shape Fancy Cut Lab Diamonds For Making Lab Diamond Earrings
Fancy Cut Lab Diamonds Description
Lab diamonds are real diamonds. Carbon is the main element of natural and laboratory-grown diamonds. The chemical and physical properties of synthetic diamonds are same as natural diamonds in terms of hardness, thermal conductivity, and strength. HTHP and CVD are the two main methods for making laboratory-grown diamonds. High temperature and high pressure method (HTHP) uses graphite as raw material. HPHT diamonds are manufactured at a pressure of 5-6 GPA (approximately the pressure produced by a commercial jet landing on a human fingertip) and a temperature of 1300-1600°C. CVD diamonds come from various gases, such as methane. They are stored in a vacuum chamber, which decomposes the molecules of the gas, and then these molecules gather on the pre-existing diamond seeds.
Round cut is the most common cut. Fancy shaped lab diamond, also known as gardener cut diamond, refers to diamonds other than standard round diamonds. The common fancy shape lab diamonds include pear shaped, marquise shaped, princess, radiant, emerald cut, heart, oval shape, etc.
Pear shaped diamond is also known as water drop shape. The diamond is pointed at the top and round at the bottom. It combines the advantages of oval cutting and round diamond cutting. Besides round cutting, it is one of the most popular special-shaped cutting methods. Tracing back to the history, the first pear shaped diamond can be traced back to the 15th century. After the baptism of time, pear shaped diamond has become more and more dazzling in the field of jewelry. Pear shaped diamond can modify the shape of the hand and highlight the beauty of the line of the female hand. In terms of cutting, there are high requirements for proportion, symmetry and diamond color.
HPHT Pear Shape Fancy Cut Lab Diamonds
HPHT Pear Shape Fancy Cut Lab diamonds are a fantastic choice for a variety of purposes. This orange pink diamond is a beautiful example of HPHT technology. Its color is VVS2 with excellent clarity and a Bow-tie effect. Its size is also very popular. Financing is available and you can choose between a variety of payment plans. Buying a diamond may be one of the most important purchases you will make and it is wise to consider the different aspects when selecting a diamond.
Color of pear diamonds
When evaluating the color of HPHT pear shape fancy cut lab stones, it is important to consider their grading method. Diamonds grown with HPHT technology are less likely to contain excess boron. Diamonds with measurable boron are called Type IIa or Type IIb. Boron is often introduced during HPHT growth as a means of removing nitrogen. Because this process is difficult and expensive, many growers opt to use HPHT. In addition to being expensive and time-consuming, excess boron in lab-grown diamonds is an indication that the grower took short cuts.
The Pear shape lab diamond is an amalgamation of the marquise and oval cuts. Its tapered point at one end and rounded bottom make it a popular choice for fine jewelry and engagement rings. The color and fire of HPHT pear shape lab diamonds are virtually identical to those of natural, earth-grown diamonds. A trained gemologist can easily distinguish a HPHT diamond from an Earth-grown stone.
Although HPHT is considered a natural process, it is not a perfect one. In fact, some HPHT diamonds may have a blue undertone. The blue nuance is not visible to the naked eye, but it cannot be hidden by a simple diamond tester. The same can be said for diamonds that are treated with other methods. For instance, a 1.2 carat pink diamond could be a lab-grown Argyle.
The HPHT treatment of a colored diamond will change its appearance by altering its refractive index. It will also affect its clarity and color. Since HPHT diamonds are HPHT-treated, the fluorescence will be less intense than natural diamonds. The color of HPHT pear shape fancy cut diamonds is a key factor in making a purchase. If a colored stone has less color, then it’s probably a fake.
Whether a diamond is natural or not, HPHT treatments are a good way to enhance its color. HPHT treatments can be performed on both natural and synthetic diamonds. You should always check the certification of a stone you’re considering purchasing. You can look for an official HPHT certificate in your local jewelry store. The process is permanent and can transform brownish diamonds into colorless diamonds.
Clarity of pear diamonds
A pear cut lab diamond is a modified brilliant cut, combining the characteristics of oval and marquise cuts. Pear diamonds are an excellent choice for engagement rings, pendants, earrings, and fine jewelry, since their cut creates the desired fire and brilliance. Below are some tips for buying a diamond:
One concern of HPHT diamonds is blue nuance. HPHT diamonds have considerable blue nuance. However, they look whiter than 99% of earth-extracted diamonds. They also carry a distinctive pattern to show the fact that they were grown in a lab. In addition, they may have been given a post-growth treatment to improve their color. Furthermore, HPHT diamonds of hues D, E, and F do not mature in the desired color, but instead develop a brown color.
HPHT can make a pear shape fancy cut look larger when it is set in a halo setting, which adds sparkle. When set in a solitaire, the pear shape diamond can be noticed more easily, because of its pointed tip. Although the clarity of HPHT pear shape fancy cut lab diamonds is identical to natural diamonds, a trained gemologist can’t tell the difference. If you are considering purchasing a pear-shaped diamond, make sure to reference an official certification before making your purchase.
While natural diamonds are often mixed with other elements to give them their color, laboratory-grown diamonds don’t. Natural diamonds take millions of years to form, but HPHT pear-shaped lab diamonds grow faster and more efficiently. During the HPHT process, a small diamond seed is placed into pure carbon, exposed to high temperatures and high pressure. This process melts the carbon and diamond forms around it. Once the crystallization process is complete, the diamond is carefully cooled to form a diamond.
Although buying a lab-grown diamond may seem like a bad idea, it’s completely safe if you ask a jeweler to check it for you. Be wary of local jewelers who bring in lab diamonds reluctantly and don’t know their product. A salesman’s rationale may be deceiving and the diamond might look good in a shop window.
Bow-tie effect
Having a bow-tie effect on a diamond is not desirable. While diamonds with dramatic bow ties will not reflect light well, they may add some character to a piece. If you are looking to buy a diamond for a special occasion, a subtle bow-tie can add to the overall appeal of the stone. It is important to examine your diamond carefully under different lighting conditions to determine if it will affect the value of the whole piece.
If the diamond’s appearance is off-centered, it may be a sign of additional clarity problems. A diamond with a bow-tie effect may also exhibit slight yellow tints, but these are likely due to the colored background. However, if you have any doubts, you can contact your diamond supplier. They will give you a video of the diamond to help you determine its quality.
A video of the diamond’s appearance is another way to assess the bow-tie effect. Unlike a still photo, a video can show the full extent of the bow-tie. And, if you can’t find any 360-degree photos of the diamond, try searching online. One website offers 360-degree video and photos of any diamond.
Another popular option is to buy diamonds that are less than 10% of the carat weight. These diamonds will be much cheaper because they will be much smaller. A well-cut diamond will not show the bow-tie effect. Moreover, it will appear larger than other stones of the same carat weight. So, even if you choose a smaller-carat-weight diamond, you can still get an impressive looking ring.
While diamonds are often purchased because of their appearance, this effect is also important when deciding whether to buy one. The Bow-tie effect on HPHT pear shape fancy cut lab diamonds is the result of a looser grading standard and a lower quality stone. The resulting diamond may look like a diamond, but it is far from ideal.
Size of pear diamonds
A pear shape diamond has a larger surface area than a round or square diamond, making it appear larger than they really are. When choosing a diamond, it is important to look for a ratio between 1.55 and 1.75. A diamond with a lower ratio may look wide or have a curled edge, which may be unappealing. If you choose a high ratio, you should ensure that the setting is secure, as this stone is more likely to chip.
The shape of a pear diamond is an amalgamation of the oval and marquise cuts. Its elongated silhouette, single point, and deep percentage are what make it desirable as a diamond shape. Pear lab diamonds are also excellent for fine jewelry, such as engagement rings, pendants, and earrings. A pear diamond’s shape will make it appear larger than it is, and it will be an ideal choice for anyone wanting a unique look for their fine jewelry.
The size of a pear diamond in an HPHT fancy cut lab diamond will depend on the carat of the stone. The higher the carat, the bigger the diamond. However, the carat weight does not affect the visual size of a lab diamond. A diamond of a higher carat will cost more than one with a lower carat weight. However, it can save you a significant amount of money compared to a naturally mined diamond.
HPHT is the best way to grow diamonds in a laboratory, because the process replicates the natural conditions of the stone in the earth. HPHT can be performed with several different technologies, but the Bar press is the most efficient for gem-quality diamonds. Developed by Russian scientists, the Bar press consists of an inner and outer anvils and applies hydraulic pressure to a growth cell with a tiny diamond seed, highly refined graphite, and a catalyst. The temperature is around 1,300 degrees Celsius.
DEF Color HPHT Pear Shape Fancy Cut Lab Diamonds 0.05ct To 0.3ct