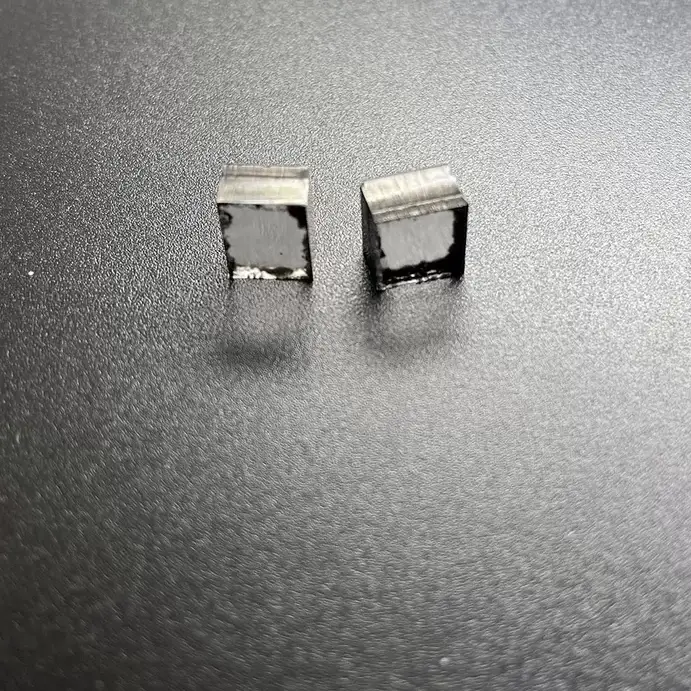
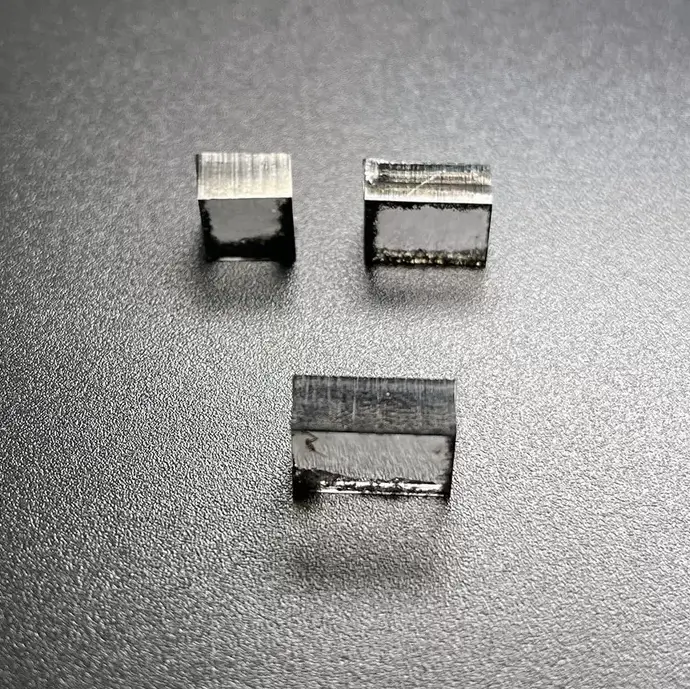
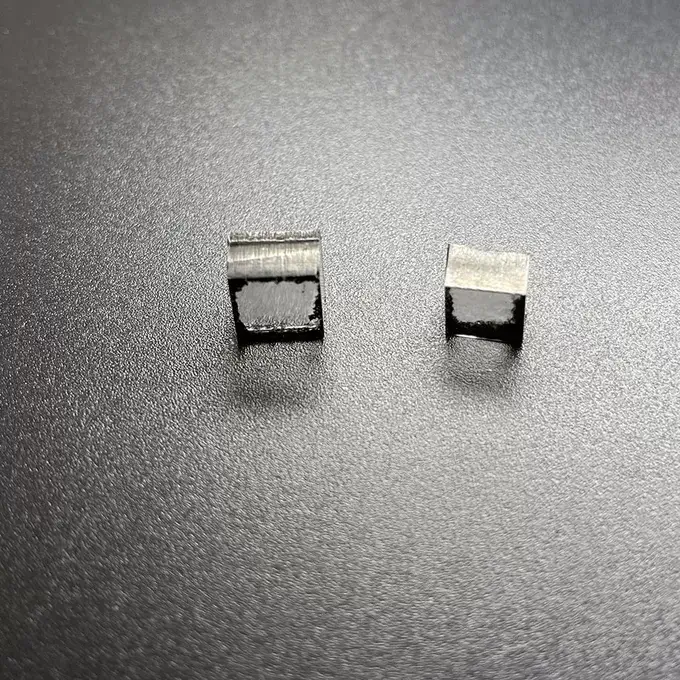
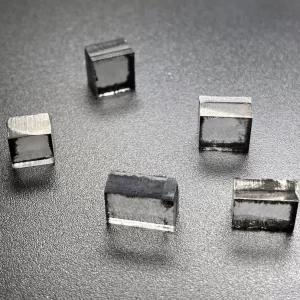
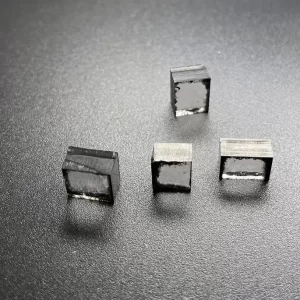
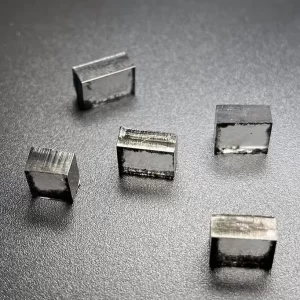
Square VS 10.0 Carat 11.0 Carat CVD Rough Diamonds Pure Uncut Diamonds For Jewelry
Square Shape VS Clarity 10.0 – 11.0 Carat CVD Rough Diamonds For 3carat Big Size Diamond Cvd Jewelry
CVD Lab Grown Diamonds Description
Lab created diamonds are grown by simulating the growth environment of natural diamonds through high temperature and high pressure or chemical vapor deposition method. The chemical, physical, atomic, and optical properties of lab grown diamonds are the same as natural diamonds. we call them laboratory-grown diamonds.
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) diamond is based on a loose natural diamond stone as the parent stone, using high-purity methane, plus hydrogen, nitrogen and other gases to assist, in a microwave oven at high pressure to make methane the same carbon as diamonds Molecules continue to accumulate on the rough diamond, and after a layer of proliferation, a transparent diamond as large as 10 carats can be formed.
Another method is HPHT(high temperature and high pressure), which uses metal elements as catalysts to simulate the temperature and pressure environment produced by natural diamonds for lab grown diamond growth.
As the first generation of diamond growth technology, high temperature and high pressure technology can completely simulate the growth process of natural diamonds, reproduce the reaction of the carbon layer on the ground, and convert graphite into diamonds.
At present, the popular high temperature and high pressure synthetic diamond equipment in the world mainly includes two side tops, six side tops and strip split ball or improved split ball.
CVD Rough Diamonds – Pure Uncut Diamonds For Jewelry
Whether you are looking for a new diamond engagement ring, a new wedding band, or a simple ring to complement your engagement ring, CVD Rough Diamonds are an excellent option. They are more expensive than natural diamonds, but the energy-saving benefits outweigh the additional costs. Moreover, they can be fashioned into fancy shapes and colours thanks to polishing techniques.
Loose diamonds are pure uncut diamonds
Uncut diamonds come in many shapes, sizes, and colors. For a unique piece of jewelry, you may opt for a loose diamond instead of a cut diamond. If you’re looking for a unique diamond, you can buy a loose one and add it to a setting, such as a ring, for a personalized touch. Loose diamonds can also be purchased separately. Blue Nile was one of the first online diamond retailers to list diamonds for sale. They don’t hold their own stock, but rather list diamonds held by other retailers. This is possible because they have strong relationships with suppliers of loose diamonds.
Although loose diamonds are pure uncut, their value depends on many factors. Diamond certification, for instance, is a major factor. While the four C’s determine a diamond’s price, many factors can influence its price, including the reputation of the vendor, the quality of information available on the site, and the merchant’s policies. A diamond’s certification will influence its price, and not all labs are created equal. Hence, diamonds with reports from second-tier labs will trade at a lower price.
Generally, the higher the carat weight, the more expensive a diamond is. But the larger the rough diamond is, the more flaws it will contain. While it’s possible to find a perfect diamond, it is difficult to obtain one. Therefore, a flawless raw diamond may be worth more than a cut diamond. The clarity grade, or “clarity,” refers to the number of natural inclusions in a diamond. While an ideal diamond has no visible flaws, a diamond with a few noticeable inclusions is still more valuable.
They are more expensive than natural diamonds
There are pros and cons to both natural and CVD rough diamonds. While natural diamonds are more expensive, laboratory created ones are more durable and resale-value-conscious. Although lab-created diamonds are more expensive than natural diamonds for jewelry, they are cheaper than their natural counterparts. The only downside is that the resale-value of lab-created diamonds is often low compared to natural diamonds.
While mined diamonds are still more expensive than lab-grown ones, man-made ones are better for the environment. Although diamonds aren’t particularly rare, mining them is still a very labor-intensive process that disrupts landscapes, wildlife habitats, and human livelihoods. Miners must sift through thousands of pounds of dirt to find a single stone. Lab-grown diamonds produce little waste, and they don’t fund conflict or funding. Consumers prefer man-made diamonds because they are a great value for their money, and they do not have any of the negative consequences associated with mined diamonds.
CVD rough diamonds are usually cheaper than natural diamonds for jewelry. They are usually 30 to 50 percent cheaper than natural diamonds. In addition, consumers can purchase larger diamonds with these gems. This makes the diamonds more affordable for everyday use. The disadvantages of the lab-grown diamonds are largely related to their quality, but the benefits of lab-grown diamonds are well worth the cost.
While the quality of CVD diamonds is not as good as that of HPHT diamonds, the process is cheaper and easier to scale. In addition to being more affordable, CVD diamonds are much more durable than HPHT diamonds. Besides, their color and clarity are much better. They can be cut, polished, and graded faster than natural diamonds. If you are looking for a new diamond for jewelry, consider the quality of the CVD diamond.
They require additional treatments
Most diamonds in the market today are treated, and CVD roughs are no exception. While diamonds treated through these processes are usually less valuable than those produced by natural mining, they are still worth more than diamonds not treated. Moreover, the permanence of treatments varies greatly. While the foil may come off in an ultrasonic cleaner, a fracture filling may become unstable if you use a jeweler’s torch. As such, you must understand the different treatments to preserve your diamond’s treatment.
In addition to the additional treatments, diamonds treated with CVD also have a higher atomic density than natural ones. However, a high atomic density makes the presence of interstitial point defects rare. Additionally, the rigid lattice of diamond leaves very little room for foreign atoms. However, small substitutional defects do exist in diamonds and may act as electron donors or acceptors. Moreover, CVD diamonds often contain non-carbon atoms such as Si, P, and S.
While conventional polishing techniques are effective in improving the clarity and color of CVD rough diamonds, these methods are technically challenging and require small samples. Although many studies have used indentation methods to measure strength of single crystal diamonds, these methods require smaller volumes of materials and are inconvenient for manufacturing. In addition, inconsistent surface preparation makes it difficult to reproduce the results. So, in most cases, additional treatments are necessary to obtain high-quality CVD diamonds.
Most CVD synthetic diamonds are brown. HPHT annealing removes the unwanted tones, but sometimes leaves visible hues on the stones. Some of the diamonds that undergo HPHT annealing may appear blue or gray under UV light. The same is true for CVD diamonds with a grayish tint. Moreover, higher temperatures may remove certain inclusions or even a brown hue.
They are less energy efficient than HTHP
The most obvious reason why CVD rough diamonds are less energy efficient for jewelry is the high amount of nitrogen they contain. While nitrogen is considered a waste byproduct, it makes diamonds more valuable. It also reduces the amount of energy required to grow a single carat. In fact, nitrogen has been shown to double the growth rate of diamonds, resulting in twice as many carats in the same amount of time. This could be significant if you want to reduce your energy consumption while making your jewelry.
Although the mined diamond industry would like you to believe that they’re a better choice, the truth is that CVD rough diamonds are more expensive. The cost is based on the size of the diamond. However, this isn’t always the case. In most cases, they’re less energy efficient than HTHP diamonds for jewelry. So which method is better?
HPHT, on the other hand, is less energy efficient than CVD diamonds for jewelry. This is because mined diamonds are grown miles below the surface of the earth, under scorching temperatures and extreme pressures. Moreover, CVD diamonds require less upfront equipment cost than HTHP diamonds for jewelry. Moreover, they may need subsequent treatment for color.
The CVD method is the most energy efficient way of creating jewelry. Compared to HTHP, CVD rough diamonds require less energy. However, they produce more square diamonds. The two methods differ a great deal in terms of how much energy they require. HTHP uses intense pressure and heat to grow diamonds, while CVD uses a vacuum chamber.
They have higher clarity grades
Although natural and CVD rough diamonds have very different growth histories, both exhibit similar grading characteristics. GIA graders use the same terms for clarity in both types of diamonds, though they are not identical. For example, a crystal or black inclusion of non-diamond carbon in a natural diamond would be called a cloud. A needle-like inclusion would be a very small crystal that is visible under 10X magnification.
Since natural diamonds are not the only types of synthetic diamonds, CVD diamonds have a higher clarity grade for jewelry than other gemstones. They also have no ethical or environmental issues. GIA has also inspected diamonds that have been produced using CVD technology. CVD rough diamonds are also cheaper than natural diamonds, resulting in significant savings on the diamond itself. They usually cost 20 to 30% less than natural diamonds.
The GIA lab observes that CVD diamonds have higher clarity grades for jewelry purposes. The laboratory uses a number of techniques to identify CVD diamonds, including photoluminescence. Some of these techniques are highly sensitive, and it is recommended to send your diamond for lab analysis. The GIA lab recommends that you send your stone to a professional gemological laboratory for analysis. A major gemological laboratory will be able to positively identify a CVD synthetic.
As mentioned earlier, diamond prices are highly variable and are largely dependent on clarity grade. Even diamonds of the same color and clarity grade can vary in price. High clarity grades are rare, and are worth more money. However, the GIA has just recently begun assigning single-grade color and clarity to lab grown diamonds. While natural diamonds do not have this issue, CVD rough diamonds are far cleaner and have higher price ranges for jewelry.
Square VS 10.0 Carat 11.0 Carat CVD Rough Diamonds Pure Uncut Diamonds For Jewelry