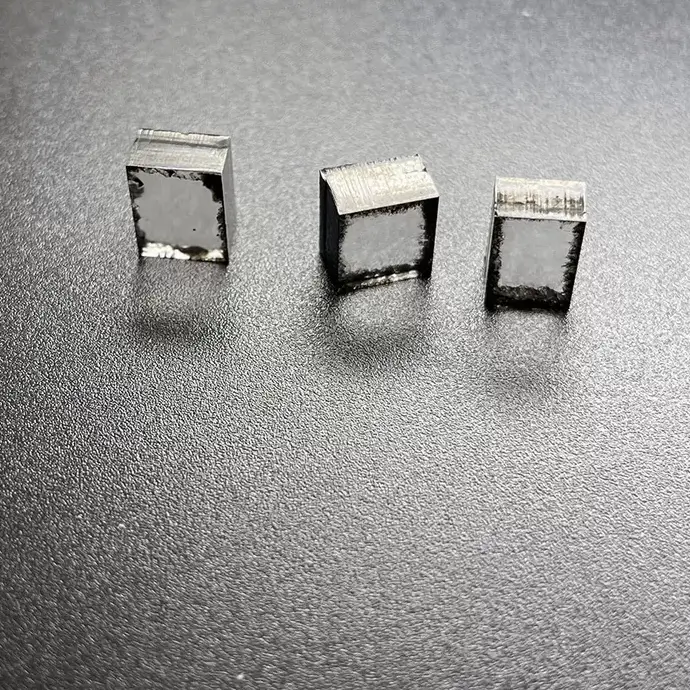
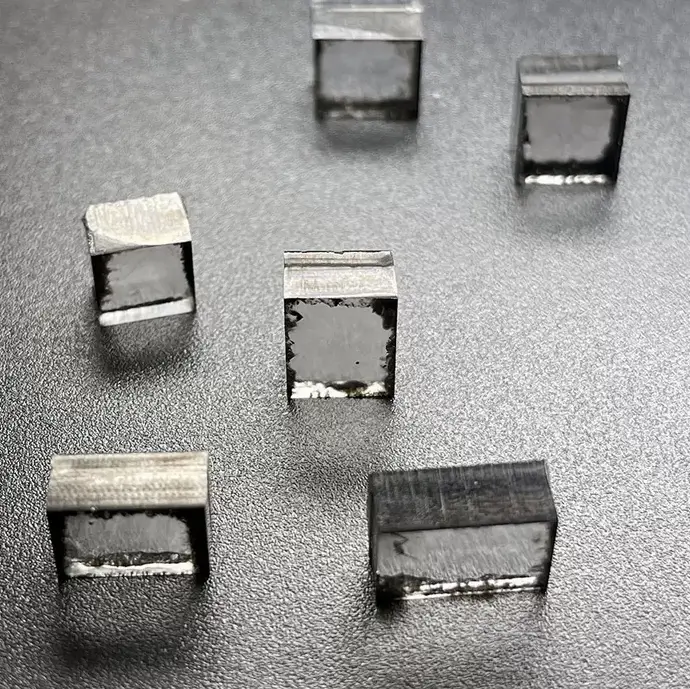
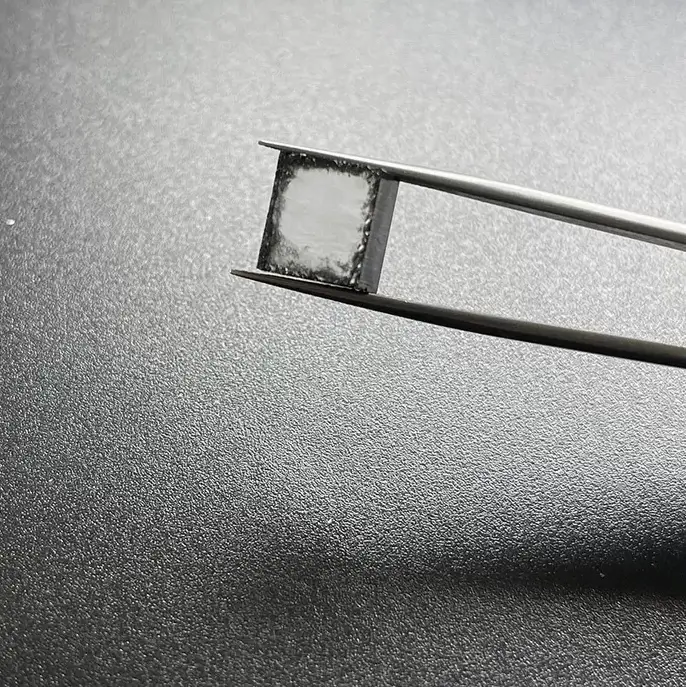
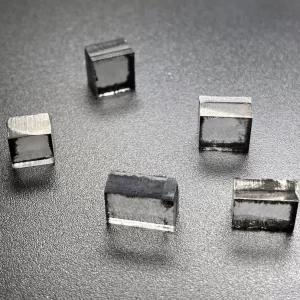
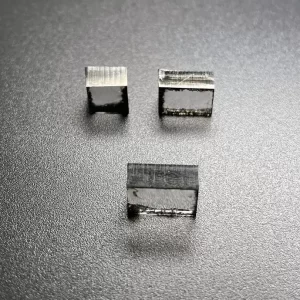
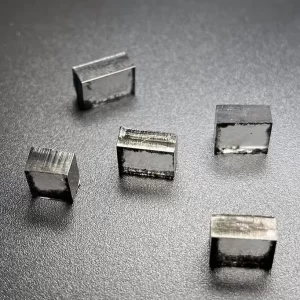
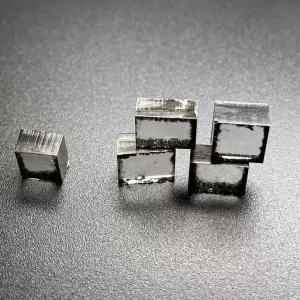
E F Color VVS VS 12Ct 12.5Ct 13Ct CVD Rough Diamonds For 4 Carat Polish Diamond
Square Shape E F Color VVS VS Clarity 12.0 Carat – 13.0 Carat CVD Rough Diamonds For Making 4carat Lab Grown Polish Diamond
CVD Rough Diamonds Description
Diamond is known as the hardest material in the world. According to the Mohs hardness scale, it is divided into 10 grades, and diamond is the highest grade. From the day when people know that diamond is composed of pure carbon, there are more and more researches on Lab Grown Diamonds. Now Lab Grown Diamonds industry has developed rapidly and is widely used in various industries.
There are two main methods to make lab grown diamonds. One is called HPHT(High Temperature and High Pressure) and another is CVD(Chemical Vapor Deposition)method.
High temperature and high pressure synthetic diamond technology originated in the 1950s, initially mainly used in aviation and military industry, in the last decade gem grade synthetic diamond in quality and cost has reached the level of marketization.
HPHT lab grown rough diamonds is produced by simulating the crystallization process of natural diamonds. When natural diamonds are formed in natural environment, there are often other elements mixed in, which makes some natural diamonds not completely transparent and will show specific colors. For example, some diamonds have a little pink, some with a little blue, some with a little bit of light yellow. Lab grown diamonds grow in the laboratory, which are less impurities than natural diamonds, so the purity and transparency will be higher.
CVD Rough Diamonds For 4 Carat Polish Diamond
There are several ways to prepare CVD rough diamonds for polishing. One way is to cut away the polycrystal with special cutters. Another method is disc machining. The planner and cutter decide which method will be more effective. The shape of the future diamonds will depend on the shape of the polycrystal. Some common shapes of diamonds are the princess cut, radiant cut, Asscher cut, and cushion cut. The corners of round diamonds are also filled with small fragments. These fragments can be cut to create small sieve diamonds.
Natural diamonds
How do you assess the purity of a 4 carat Polish diamond? CVD rough diamonds can have numerous ingrown carbons, polycrystals, and blemishes. A skilled diamond cutter will know which of these flaws will be hidden by the crystal and determine the most efficient way to create a polished gem. A rough diamond of 2.00 carats could result in two gems of.50 carats each if the crystals are cut and polished differently. In the end, the cutter will choose the gem that offers greater value.
Scientists began growing diamonds in the mid-1950s using the high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) method. Although the first diamonds grown in a laboratory were too small to be used for jewelry, the technology has now been developed to the point that it is used for industrial and jewelry purposes. Unlike natural diamonds, synthetic diamonds do not have the impurities that naturally occur, and their purity and transparency is superior.
The process used to grow CVD diamonds is a relatively new technique. The growth of the diamond occurs inside a chamber that contains a mixture of carbon-containing gases. The gas molecules are broken down by a microwave beam and begin to diffuse towards the seed plates. The process takes several weeks, and the size of the chamber and seed plates determines the number of crystals that will form. A few of the rough diamonds will be tabular, and these will often show black graphite rough edges. A heat treatment prior to faceting will remove these features.
CVD rough diamonds for 4 carat polish gemstones are considered to be of good quality and are not expensive. The colour of CVD rough diamonds without post-growth treatment is typically no better than H. However, some diamonds are sold as grown or undergo post-growth treatment, resulting in an upgrade in colour. For example, a 4 carat Polish diamond obtained from a CVD rough stone may have a light pink hue.
Synthetic diamonds
While looking for CVD rough diamonds for 4 carats, you should consider the color and clarity of the stone. A gemologist will be able to identify many of these features and help you determine their worth. A poorly colored Polish diamond can have flaws, and an incorrect color estimate can cost you thousands of dollars. Inclusions can also affect a Polish diamond’s sparkle and transparency.
Impact toughness is one of the most important indices of synthetic diamond quality. Depending on its hardness, an improved CVD polish will increase the diamond’s impact toughness, or ‘crack resistance’. After polishing, the weight of the diamond will remain unchanged. Finally, the diamond’s color and strength will be extracted. This process will produce a diamond that is a more durable option than a conventional Polish diamond.
The most common type of CVD-grown rough diamonds is called an HPHT rough. This form of diamond grows in one crystal, and its seeds are visible. ACVD rough diamond may contain metallic inclusions. Some of the larger metallic inclusions can be picked up by magnets. During the growth process, diamonds are surrounded by a protective layer of gas called nitrogen. ACVD polish will improve the diamond’s transparency and clarity by one or more grades.
Although CVD rough diamonds are the most popular form of Polish diamonds, they do not come with the same quality as a Polish diamond. CVD rough diamonds are usually more expensive than natural polish diamonds, which is why the color and quality of the Polish diamond is so important. The color of a diamond is directly related to how many exposures it receives before it hardens. But the quality of the rough diamond will ultimately be dependent on how well it is polished.
Cost of cutting and polishing
The cost of cutting and polishing rough diamonds depends on several factors. The rough diamond’s carat and state can affect the final cost. Where the diamond is found also has an effect on the price. Cutters in some regions may charge less than in others. Some rough diamonds are less expensive than polished ones, though this can vary. Generally, the price of a finished diamond is around two to three times higher than the cost of its rough form.
The process of cutting and polishing a diamond is very expensive, so you should know exactly how much you can spend. The better the quality of the cut, the higher the price. Also, remember that rough diamonds don’t sparkle and are not worth as much as a finished one. Therefore, the quality of the rough diamond determines the price of the finished diamond. The more clarity and color a diamond has, the higher its price.
Once the rough diamond is cut and polished, the process of cleaving and sawing involves a diamond cutting tool called a tang. The sawing and cleaving processes may have to be performed first to prepare the stone for the next step. While the sawing and cleaving steps are similar, laser cutting is more accurate and quicker, but both processes require the use of lasers.
The process of cutting and polishing rough diamonds has evolved over time. Today, more diamond growers are offering calibrated polished diamonds to the jewellery industry. While the yield of such polished diamonds is lower than that of parcels, they are more liquid and have a higher price. These factors all contribute to the high cost of diamond cutting and polishing. For a diamond to be valued at the maximum value, the process of cutting and polishing it must be done correctly.
Cost of cutting and polishing in Surat
Increasing cost of raw diamond material has affected Surat’s diamond industry, which employs more than 500,000 people. The price of diamonds has increased sharply, leading to lower purchases of rough by exporters. Many diamond polishers are now working only three days a week, and some are working only three days. The cost of rough diamonds in Surat has increased by as much as 20% since the outbreak of the disease Omicron in the diamond mining region in Ukraine in February 2022. Thousands of workers are now working three days a week.
The process of cutting and polishing rough diamonds begins with feeding the stones into a computer, which runs specialised 3D imaging software. These software programs are designed to cut diamonds with the greatest proportion of sparkle and brilliance. These programs can cost several crores or tens of millions of dollars. The software recommends the best cuts for the diamond, which are then manually verified, if necessary, and presented to the senior design team.
A significant contribution to the growth of the diamond industry in India has been the creation of jobs in the area. In Surat alone, about 500,000 jobs have been created. Many of these jobs are unskilled and give people in rural areas the chance to rise above the poverty line. The average diamond cutter earns around five times the per capita income of his or her community. In addition to creating jobs, the globalization of the diamond industry has encouraged India to adapt cutting-edge technologies and improve its business practices.
Despite the heightened cost of rough diamonds in the region, the Surat diamond market has shown signs of recovery in early August. Demand has steadily improved in the US, China, and parts of Europe. As the outbreak of COVID-19 decreased, diamond cutting and polishing activities in Surat began to pick up. This resulted in nearly 5,000 manufacturing units becoming operational. While these factories are now operating at nearly 70 percent of their capacity, the government has given diamond cutting units greater flexibility. However, they are still required to comply with a rigid set of guidelines, including mandatory Covid-19 tests.
Price of cut and polished diamonds
The pricing of cut and polished diamonds varies widely, mainly because of their quality. The quality of diamonds is largely dependent on their cut, color, clarity, and carat weight. Higher quality diamonds generally command higher prices. However, the price difference between lower and higher grades of cut is relatively small, and the difference is more pronounced in larger carat sizes. It is important to do some preliminary research on the prices of diamonds before buying one.
The price of diamonds varies widely depending on their shape, carat weight, and other factors. A two-carat round diamond may cost $2,500 or $7,400, but a 0.5-carat diamond can cost $1250. As you increase the size and quality of the diamond, the per-carat price also increases. However, this price increase is still within a reasonable range. The best place to buy a diamond is near the intersection of quality and value.
Some cities have traditionally been major centers for diamond cutting and polishing. While Belgium and Israel still have an active diamond industry, they have been outsourced to Asia due to labor costs. In Surat, India, for example, cutting diamonds is a $1.8 billion industry. The city is now home to over 90% of the world’s diamonds. However, despite its soaring popularity, there is still a large shortage of small diamonds in these two cities.
A rough diamond price list is also available for a diamond. It is an easy to use tool that uses information on weight, color, and clarity to determine the purchase price. This index allows consumers to compare prices of cut and polished diamonds at different prices. If you want to find the best value, shop around and see which ones have the lowest prices. It is important to compare prices online and in brick and mortar stores.
E F Color VVS VS 12Ct 12.5Ct 13Ct CVD Rough Diamonds For 4 Carat Polish Diamond