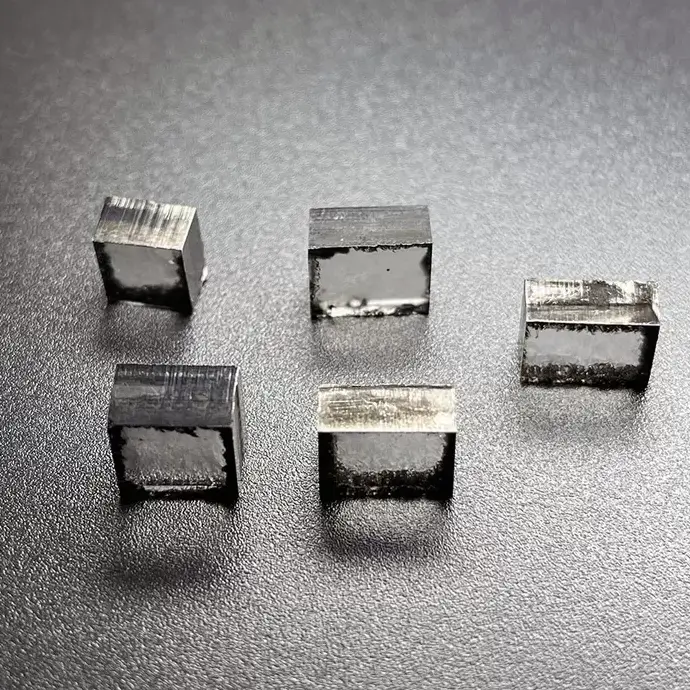
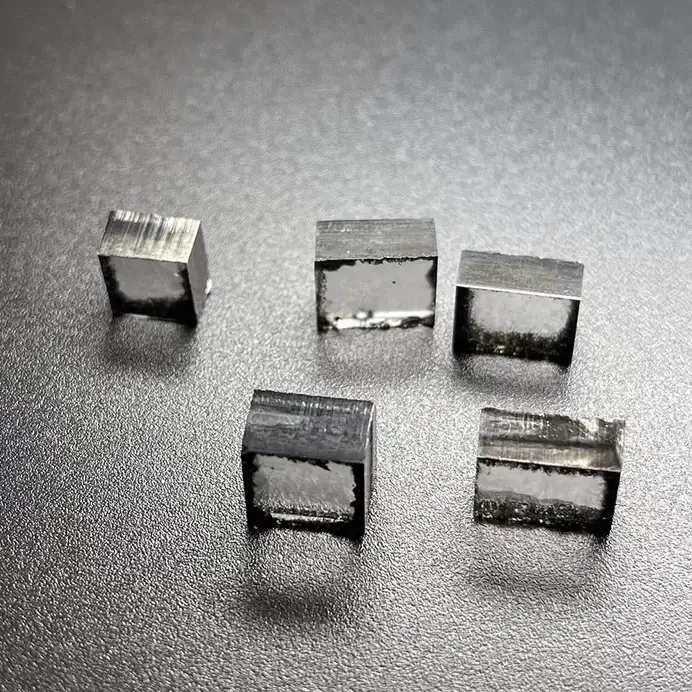
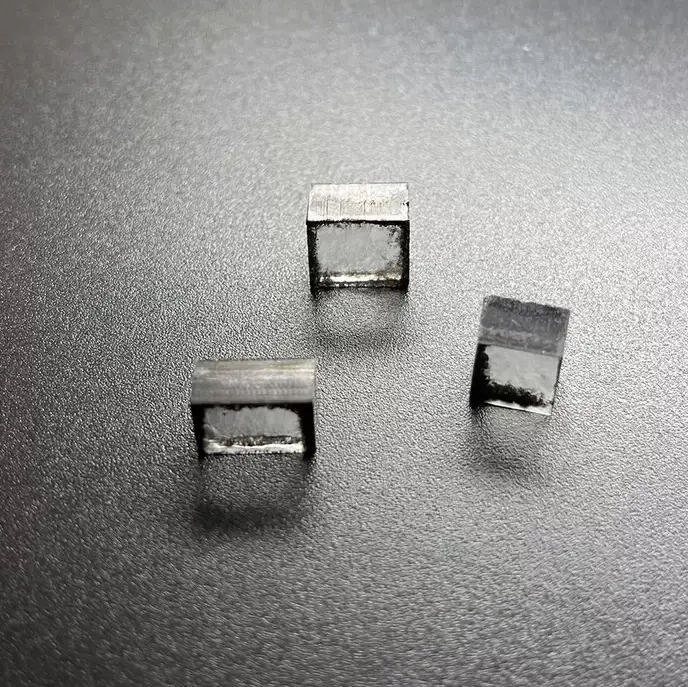
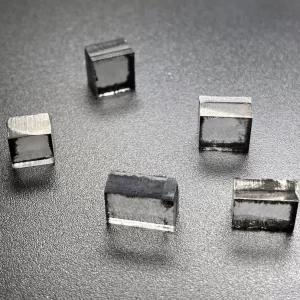
EFG Color 10mm 12mm CVD Diamond Lab Grown 8ct 12ct For DEF Loose Diamond
Square Shape EFG Color 10mm – 12mm EFG Color Cvd Diamond Lab Grown For DEF Color Loose Diamond Cutting
CVD Lab Grown Diamonds Description
Laboratory diamonds, also known as lab grown diamonds, man made diamonds and synthetic diamonds. At present, there are two main methods to create lab grown diamonds: HPHT(High Temperature and High Pressure) method and CVD(Chemical Vapor Deposition)method.
Both natural diamond and lab grown diamonds are pure carbon crystals, and their physical, chemical, crystal structure and optical properties are same. Due to the different formation conditions, the nature of natural diamonds and cultivated diamonds are also different. However, natural diamonds grow into octahedral crystals (eight equilateral triangular facets), while cultivated diamonds can grow into both octahedral and cubic crystals (six square facets).
HPHT stands for High Pressure High Temperature Method, which is a main method used in laboratories to make diamonds. This diamond growth process requires carbon to be exposed to extreme temperature and pressure conditions, which simulate the extreme heat and pressure conditions when natural diamonds are formed in the depths of the earth.
High temperature and high pressure synthetic diamond technology originated in the 1950s, initially mainly used in aviation and military industry, in the last decade has achieved a qualitative leap in technology, gem grade synthetic diamond in quality and cost has reached the level of marketization.
CVD Diamond Lab Grown 8ct For Loose Diamond
You may be wondering about the price of a lab-grown diamond. The price range of a lab-grown diamond varies depending on its size, clarity, and color. Read on to know more. This article outlines the cost and resale value of a lab-grown diamond. This article is not intended to replace a diamond’s appraisal. It is a guide for potential buyers.
Cost of lab-grown diamonds
The price of CVD lab-grown diamonds has been falling dramatically since the industry started in 2008. In 2008, the equivalent gem-quality diamond cost nearly $4,000 per carat. This trend is likely to continue as efficiencies improve and new competitors enter the marketplace. This technology will eventually become as mainstream as mined diamonds. For now, however, lab-grown diamonds can be purchased for as little as $300 per carat.
The natural diamond industry consists of miners, traders, polishers, jewelery makers, and retailers. The man-made industry, on the other hand, controls many functions within one company. Its German-born Chief Executive, despite the recent rise in price of man-made diamonds, has refused to reduce prices due to Lightbox. Ultimately, consumers will benefit from lower prices and the fact that man-made diamonds have more value than natural stones.
CVD lab-grown diamonds are generally cheaper than natural diamonds, but the differences in price and quality are substantial. While natural diamonds tend to be rare, they still have a high resale value. If you plan to sell your diamonds in the future, they may not hold their value as long as natural ones. A lab-grown diamond, on the other hand, may not hold its value over time. This means that the resale price could depreciate over time as a result of a flooded market.
The CVD process relies on ionisation to break the molecular bonds in a diamond seed. The pure carbon released from this process attaches itself to the seed diamond and forms atomic bonds with it. This process continues for a few weeks and produces a larger diamond that is nearly identical to the diamonds formed underground. One carat of CVD diamonds takes about a month to grow. General Electric developed the first CVD lab-grown diamond in 1955. The first gem quality reports were met with skepticism and were not verified until a few years later.
Another difference between natural and lab-grown diamonds lies in their environmental impact. In addition to their high price, lab-grown diamonds are significantly more sustainable. While mined diamonds are often used for jewellery, CVD lab-grown diamonds are also being used for environmental remediation. Adding boron to the diamond growing process helps it conduct electricity, which oxidises the toxic organic compounds and converts them into biodegradable forms.
Carat size
If you’re looking for an elegant yet affordable engagement ring, you might want to consider a lab-grown diamond. The price tag of these diamonds is considerably lower than those found in the rough. And because they are man-made, they also have a lower environmental footprint than diamonds from traditional mining operations. In addition, CVD diamonds do not come from conflict zones. This is an important aspect for ethical shoppers and those who care about the environment.
While there is no real difference in the appearance of a CVD diamond, it will definitely affect its price. If you’re looking for a diamond in a larger size, you may want to consider a loose diamond. However, note that a CVD diamond will be more expensive than a natural diamond. For this reason, it’s important to shop around before you make a decision.
Buying lab-grown diamonds with the intention of selling them is never a good investment. However, if you’re planning to sell your engagement ring, you may want to check the resale value of the diamond. Because lab-grown diamonds are still a relatively new product, it’s not easy to find a retailer who will accept your lab-grown diamond for resale. In these cases, it’s best to research the available options online.
While the price of a natural diamond is higher, the prices of a lab-grown diamond are significantly lower. For example, a one-carat lab-grown diamond can cost $3,300, compared to $4,600 for an equivalent mined diamond of the same size. That’s a lot of money to save, and you can pay for it before the wedding or honeymoon.
Purchasing a diamond that has been lab-created has several disadvantages. First, resale value is very low. You’ll probably never sell it on eBay, or sell it for more than 50% of what you paid for it originally. This means that you won’t be able to make a profit if you decide to sell it. Second, reselling a lab-created diamond doesn’t have a high resale value. Even if you find a diamond that is worth your money, you’ll likely be stuck with an ugly and cheap stone.
Color grade
There are several different ways to grade a diamond. In most cases, lab-grown diamonds will receive a VS clarity grade. The best way to determine the clarity grade of a diamond is to look at it under a 10X magnification. A diamond with an E color grade will look more like a D, and a diamond with a D color grade will look like a F. Inclusions that affect the stone’s clarity grade can be easily seen under a 10X magnification.
Another method of determining a diamond’s color is to look at its fluorescence. A lower color grade will appear whiter if it has fluorescence. Besides the color, the setting can also play an important role. When choosing a setting, it is important to find a stone that complements the setting and makes the diamond look even more beautiful. In addition, consider the cut and clarity of the diamond. It should complement or enhance the setting, not detract from the overall appearance.
The carat size of the diamond is another factor to consider. Using a laboratory-grown diamond can make your diamond bigger or smaller. The carat size is also an important factor in the look of a diamond. A larger carat means a more expensive diamond. For these reasons, it is important to understand the difference between a natural diamond and a lab-grown diamond.
As far as color goes, the G to I range is the most desirable for most consumers. These stones are more affordable than natural diamonds and are whiter than those in the D to F range. They are also ethical and have fewer inclusions and blemishes than natural diamonds. Whether you choose a synthetic diamond or a natural stone, it is important to understand how to grade it correctly. The GIA has recently ruled in favor of synthetic diamonds, which has sparked an increase in consumer demand.
The GIA and AGS have both changed their policy on grading lab-grown diamonds. The AGS ceased grading synthetic diamonds in 2013 citing a lack of demand. It will resume grading synthetic diamonds in August 2020. Prior to the IGI’s policy change, IGI had been the most common choice for lab-grown diamond grading reports.
Resale value
If you are considering buying a loose diamond, you may be wondering about the resale value. This is because diamonds can have very little value if they were not grown in the United States. This can make the sale process a bit complicated, especially if you are not a US citizen. Diamond retailers must follow Know Your Customer laws as part of the US Patriot Act. These laws are intended to discourage the use of diamonds as a means of money laundering.
While diamonds created in a laboratory have a lower resale value than mined diamonds, there is still a difference between mined and lab grown diamonds. While they may look uncannily similar to real diamonds, only a certified gemologist can distinguish a lab created stone from a natural one. The truth of the diamond is on the girdle. Lab grown diamonds have an inscription on the girdle indicating they are a synthetic.
The difference between a lab grown and a natural diamond is less than a carat. However, it can be significant enough to warrant a higher price. For example, an 8ct diamond may be worth more than an eight-carat natural diamond, but a 10 carat diamond will cost a much higher price. Ultimately, the price of the diamond will determine its resale value.
If you are buying a diamond for resale, you’ll want to know that the resale value of a lab grown diamond will be significantly lower. Unlike a mined diamond, a lab grown diamond will not retain its value and can be sold for less on eBay. If you are interested in resale value of a CVD Diamond, make sure you check with a jeweler.
If you are considering purchasing a CVD Diamond, you may want to consider buying a loose diamond first. Its pure, transparent, and high-quality properties make it the ideal choice for resale. If you are not sure about purchasing a loose diamond, a second opinion is always beneficial. It may just change your mind. Afterwards, you will know that you should be buying a diamond of a higher grade.
EFG Color 10mm 12mm CVD Diamond Lab Grown 8ct 12ct For DEF Loose Diamond