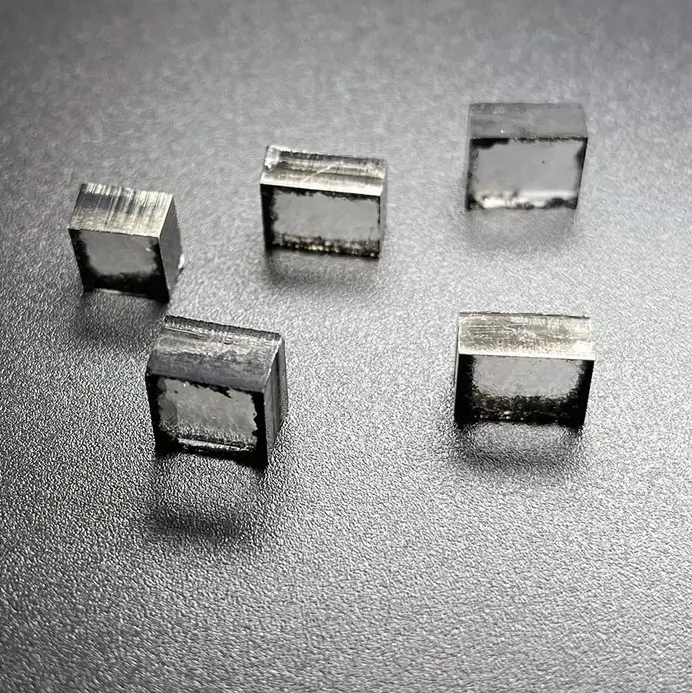
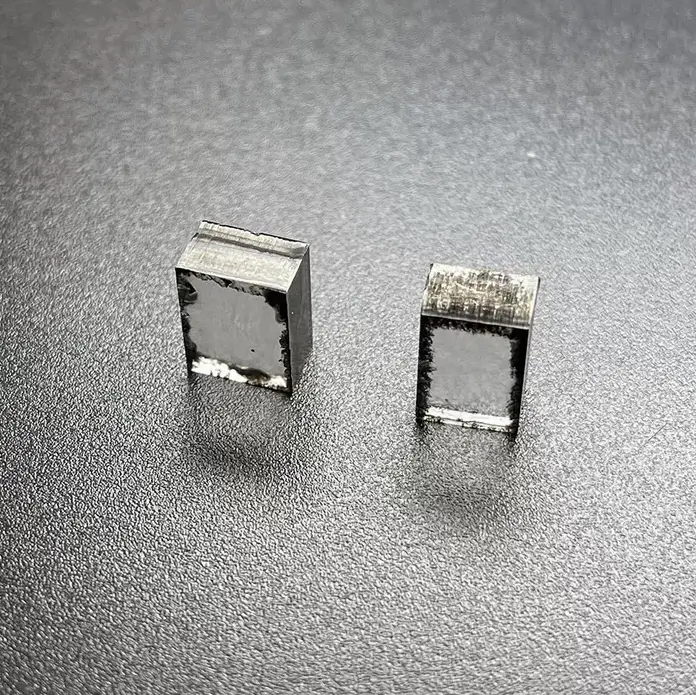
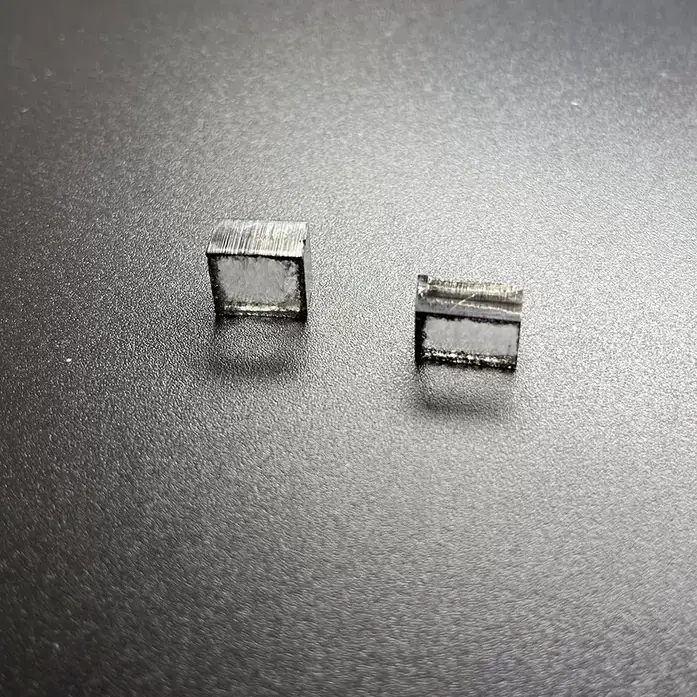
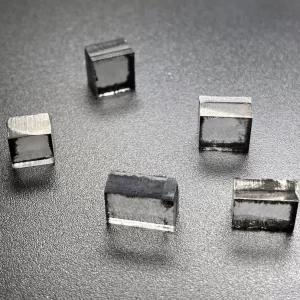
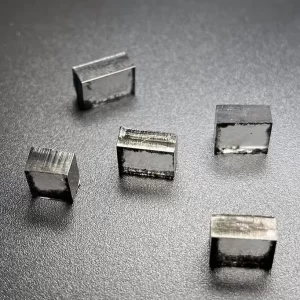
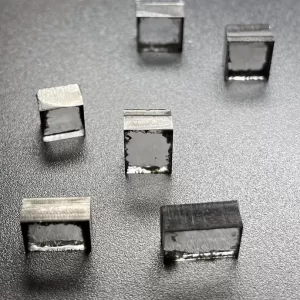
11mm 13mm E F G H I Color CVD Raw Uncut Diamonds For Loose Diamonds
Square Shape EF Color 11mm – 13mm E F G H I Color Raw Uncut Cvd Diamonds For Cutting And Polishing Loose Diamonds
CVD Rough Diamonds Description
Laboratory-grown diamonds, also known as laboratory-made diamonds, man-made diamonds and synthetic diamonds, are pure carbon diamonds that simulate the natural growth process of the earth under strictly controlled laboratory conditions.
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) diamond is based on a loose natural diamond stone as the parent stone, using high-purity methane, plus hydrogen, nitrogen and other gases to assist, in a microwave oven at high pressure to make methane the same carbon as diamonds Molecules continue to accumulate on the rough diamond, and after a layer of proliferation, a transparent diamond as large as 10 carats can be formed.
HTHP synthetic diamonds are often cubes, octahedrons, and the combination of the two; the color is often yellow, yellowish brown, and the internal features such as colored bands and metal inclusions are common. The unmelted metal inclusions are needle-shaped, flake-shaped, and small columnar. Or irregular appearance with metallic luster, which makes synthetic diamonds magnetic.
Synthetic diamonds usually have no fluorescence under long-wave ultraviolet, and often have yellow, green-yellow, orange-yellow fluorescence under short-wavelength. Synthetic diamonds have characteristic banding under ultrashort-wave ultraviolet or cathode rays. Different growth areas show different colors of fluorescence.
CVD Raw Uncut Diamonds For Loose Diamonds
There are two types of diamonds: natural and lab-created. Natural diamonds are mined from the earth, while lab-created diamonds are created by chemical vapor decomposition. Natural diamonds are the more expensive of the two, but they’re cut and polished just like their synthetic cousins. So which is better? This article will explain the differences between natural and lab-created diamonds.
Natural diamonds are mined from the earth
Before they’re cut, diamonds resemble cloudy rocks. Their chemical and structural makeup is largely unknown. Isaac Newton suggested diamonds were formed from carbon, but many doubted his discovery because of their cloudy appearance. In 1797, Smithson Tennant confirmed diamonds were indeed composed of carbon. The diamond industry has evolved to create an elaborate process to cut and refine loose diamonds.
For this process to be completed, ultra-pure carbon-rich gases, such as methane, are used. These gases are then heated and broken up into atoms, which then fall into the diamond substrate and form layers of the rough diamond crystal. This process takes about five to 10 weeks and replicates the conditions that diamonds grow in their natural environment. Machines can build sixty thousand atmospheres of pressure to make the diamonds.
In the past, De Beers controlled the majority of the world’s diamond production. In fact, it owns the Argyle mine, which once produced 42 tons of diamonds per year. The Argyle diamond mine in Australia is the richest diamantiferous pipe in the world. However, there is still no end to the exploration of diamond-bearing pipes.
While natural diamonds are colorless, the diamonds created by this process contain trace amounts of nitrogen. This makes diamonds slightly yellow, depending on the nitrogen type and concentration. Depending on the diamond’s color, the Gemological Institute of America labels them ‘normal’ and classifies them as ‘Y’, or light yellow. Diamonds with a higher degree of yellow or brown color are called ‘Fancy’ and must be graded accordingly.
Although natural diamonds have more inherent value, most of the diamonds found in the earth are not gem quality. They can be mined only to a size of 200 milligrams and 0.007 ounces. For this reason, diamonds bigger than four carats are almost guaranteed to be natural. This is because most synthetic diamonds cannot grow any larger than four carats. Moreover, sentimental value may surpass retail value. Therefore, when purchasing a diamond, consumers need to consider the environmental and ethical implications of the mining process.
They are cut and polished in the same way as natural diamonds
There are many different types of diamonds. A diamond that hasn’t been cut or polished is a “raw” diamond. This type of diamond hasn’t been treated since it was discovered. This type of diamond is often higher in quality than those sold in jewelry stores because it has not undergone any processing. While the majority of the world’s production is destined for jewelry, the remaining 80% of diamonds are used for industrial purposes.
Unlike polished diamonds, rough diamonds are less expensive. A ring made from a single carat of raw diamond can cost only a few hundred dollars, while a ring with a polished diamond can cost several thousand dollars. The best part is that these diamonds come from conflict-free mines, so you can feel good about purchasing one of these. Rough diamonds look like water-based quartz pebbles and are often brown or yellow in color.
While natural diamonds form in the earth’s mantle, lab-grown diamonds are created under controlled conditions in a laboratory setting. Natural diamonds are made millions of years ago under conditions of high pressure and temperature. After that, they are polished and cut in the same way as natural diamonds. They are then graded and certified the same way as natural diamonds.
When purchasing loose diamonds online, be sure to check for a gemological certificate. The certificate will tell you if the diamond you are purchasing is a natural diamond or a lab-grown one. When shopping online, make sure the diamond has been graded by a GIA-certified gemological lab. If you’re unsure, don’t buy it. GIA-certified diamonds are a reliable option, but you should be cautious.
The next time you’re thinking about buying a loose diamond, look into the price. It’s possible to find a diamond for much less than the equivalent of a natural diamond. You can get a 0.5 carat natural diamond for about the same price as a $1500 lab-made one. And, of course, there’s a sense of class.
They are cheaper than natural diamonds
While natural diamonds are naturally rarer, lab-grown synthetic stones are a great way to save money on your jewelry. Buying a diamond of the same quality as a natural one could cost as much as $6,800, but the lab-grown diamond would cost as little as $2300. You may even be able to resell it for as low as $50!
Despite the similarities between natural and lab-grown diamonds, the two can have very different appearances. Natural diamonds usually have octahedral crystals with eight equilateral triangular faces, whereas CVD and HPHT diamonds have only cubic faces. Natural diamonds are much cheaper, but lab-grown diamonds may contain some trace amounts of other substances.
The carbon structure of lab-grown diamonds is identical to that of a natural diamond. However, unless you own expensive testing equipment, it is difficult to distinguish a lab-grown diamond from a natural one. A diamond that is distinctly different from a lab-grown diamond will emit a strong phosphorescent glow. However, a diamond that is artificially created might not hold its value as well as a natural diamond.
The manufacturing process is similar to the one used to create natural diamonds. The only difference is the way in which they are made. A natural diamond is formed billions of years ago under tremendous heat. It then traveled up the earth’s surface in volcanic pipes. It can travel up to 100 miles of molten rock! That’s three times deeper than a typical volcano!
If you’re thinking of buying a diamond, keep in mind that a rough has many flaws that can affect its price. For example, a large rough might require extensive cutting to create a small polished diamond. Conversely, a small rough with symmetrical characteristics will likely be cheaper. However, the more flaws in a rough diamond, the less it is worth.
Lab-grown diamonds are similar to natural diamonds in appearance. They are created within a few weeks of the seed of a real diamond. This means that they are a great choice for those wanting to save money on their jewelry without sacrificing quality. The cost of CVD Raw Uncut Diamonds for loose diamonds is significantly lower than natural diamonds. And they’re also far more ethically sourced than natural diamonds.
11mm 13mm E F G H I Color CVD Raw Uncut Diamonds For Loose Diamonds