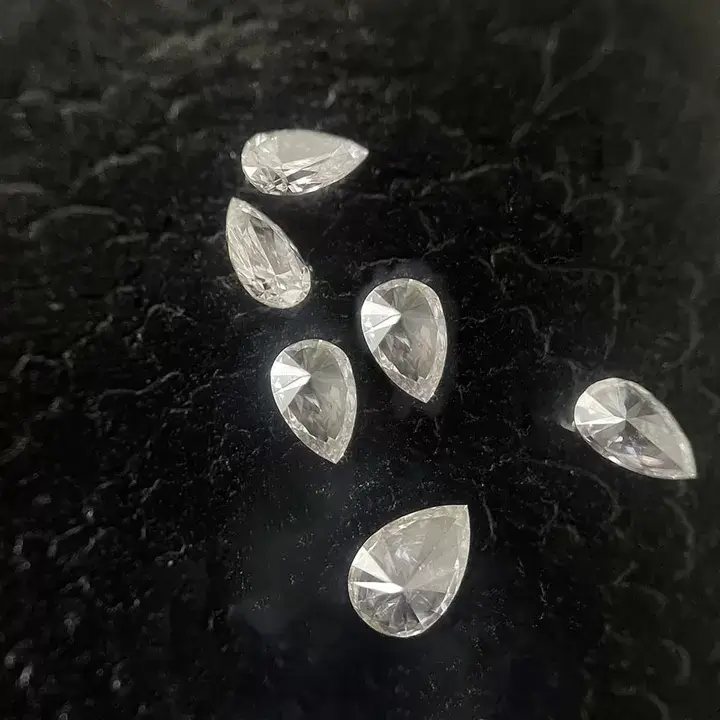
CVD Pear Shaped Lab Created Diamond FGH VS
Pear shape CVD diamond
The pear cut, with its teardrop shape, creates a subtle slimming effect on your finger.Created in the 1400s, the pear cut diamond still retains its popularity today.The pear has a similar faceting structure to the round brilliant cuts. Because of this, it retains that coveted fire and brilliance that makes a diamond sparkle.
Fancy Cut Lab Diamonds Description
Lab diamonds are real diamonds. Carbon is the main element of natural and laboratory-grown diamonds. The chemical and physical properties of synthetic diamonds are same as natural diamonds in terms of hardness, thermal conductivity, and strength. HTHP and CVD are the two main methods for making laboratory-grown diamonds. High temperature and high pressure method (HTHP) uses graphite as raw material. HPHT diamonds are manufactured at a pressure of 5-6 GPA (approximately the pressure produced by a commercial jet landing on a human fingertip) and a temperature of 1300-1600°C. CVD diamonds come from various gases, such as methane. They are stored in a vacuum chamber, which decomposes the molecules of the gas, and then these molecules gather on the pre-existing diamond seeds.
After polishing and cutting lab-grown diamonds are same as natural diamonds. they have the same brightness and fire.
Round cut is the most common cut. Fancy shape diamond is different from round cut diamond. After cutting, it has different shapes, such as princess diamond, heart diamond, oval diamond, pear diamond, etc. Fancy diamond cutting began in ancient times, and has become a trend and fashion nowadays.
Water drop cutting, also known as pear cutting, is a hybrid cutting method. Based on the traditional structure of round bright diamond, it combines the advantages of oval cutting and olive point cutting. The cut gem looks like a crystal clear tear, with a round end and a sharp end. Compared with other shapes of diamond, the ratio of length to width of water drop shape diamond depends on personal preference. Many shapes are acceptable, and the appropriate ratio of length to width of water drop shape diamond is 1.50-1.75.
ACVD Pear Shaped Lab Created Diamond
ACVD stands for Chemical Vapor Deposition, and the diamonds it produces are a great way to get the best value for your money. The most popular lab created diamonds are outlined in this guide, with prices starting at around $200. Blue Nile is the best place to buy lab created diamonds, but you can also find them at James Allen. These sellers have stellar reputations and consistently receive positive reader feedback.
Blue Nile is the best place to buy lab-created diamonds
When shopping for a lab-created diamond, choosing a reputable retailer is crucial. The three best places to buy lab created diamonds are Blue Nile, James Allen, and Clean Origin. These three vendors consistently receive good feedback from readers and have the most impressive inventory of lab created diamonds. Whether you’re looking for a solitaire diamond or a flashy halo, you’ll find everything you need here.
When buying lab-created diamonds, be sure to pay attention to cut and clarity. While most lab created diamonds are colorless to the naked eye, it’s important to read and review the diamond carefully before purchasing. However, you don’t necessarily need to seek the highest color grade possible. Diamonds in the F-H range will appear white in any setting.
Another reason to choose a lab-grown diamond is the sustainability aspect. A CVD diamond has lower environmental impact than a conventional diamond, as it does not require open-pit mining. The process requires enormous amounts of energy, and most diamonds produced in these regions do not have access to hydroelectricity. The power that runs the machinery for lab-grown diamonds is generated from fossil fuels. Despite the claims of environmental benefits, most lab-grown diamonds are produced in remote regions with very little or no hydroelectric power.
When searching for a lab-grown diamond, it’s important to know about the benefits and drawbacks of both types. Most lab-grown diamonds are eco-friendly, and are much cheaper to produce than natural diamonds. Buying a lab-grown diamond from a reputable place is the best way to protect the planet. If you are not sure about the benefits of buying a CVD pear-shaped diamond, research your options thoroughly.
A lab-grown diamond can last as long as a natural diamond if properly cared for. The process is much faster than with a mined diamond. Moreover, many lab-grown diamonds are formed using renewable energy sources and zero emission foundries. This makes them environmentally friendly as compared to natural diamonds. If you’re looking for a lab-grown diamond, James Allen is the best place to buy it online.
A natural diamond of the same weight will cost $14000. On the other hand, a lab-grown diamond can cost only $48% of this price. This means that a lab-grown diamond is an affordable choice for anyone looking for statement-making jewelry. In addition to being affordable, these diamonds are also available in different color shades. These colors are cheaper than natural fancy colored diamonds.
James Allen offers 360deg high-definition photographs of every diamond
When shopping for a new engagement ring, a traditional shopping experience can be limited. You’re often limited to a small selection of diamonds and may make a decision without fully understanding it. James Allen has revolutionized the way people buy fine jewelry by using their patented Diamond Display Technology. This allows consumers to view diamonds in high-definition and closely examine the spec sheet and details.
If you’re looking for a diamond with a superior color, look no further than James Allen. They feature over 75,000 loose lab diamonds, including an impressive selection of colored diamonds. Their ring-making process uses recycled metal and responsibly sourced natural wood. Clean Origin also boasts a strong social mission, giving back to mining communities and rainforest conservation efforts.
If you’re looking for a diamond with an ideal cut and polish, choose a cushion-cut design. James Allen’s 0.44-carat Cushion Modified Diamond looks like crushed ice when light passes through it. Despite its small carat weight, this diamond displays remarkable qualities, including an intense pink quality. It also sparkles more than any other diamond with the same shape and carat weight.
Cost of lab-created diamonds
There are a few things to consider before buying a diamond ring, whether it’s a natural or lab-created one. Natural diamonds are the most expensive diamonds in the world, and lab-grown ones are comparatively cheaper. Nevertheless, they do not retain the same value after the purchase. Unless you’re planning to sell it at a later date, you’ll be unlikely to make any money at all. While a lab-grown diamond won’t resell for a huge profit, a natural diamond can be resold for more than half of its original price.
There’s a lot of controversy surrounding the cost of lab-grown diamonds. Fortunately, technology has improved in recent years, making them a far better option. Diamonds made in labs have the same quality as natural ones, but their price is considerably lower. Since the manufacturing process is controlled and more efficient than the natural process, a lab-grown diamond will be more affordable than a natural one.
Although James Allen doesn’t sell loose lab-grown diamonds, they do have a wide selection of lab-grown stones for sale. The site’s collection includes both colored and colorless diamonds. The company also offers affordable colored lab-grown diamonds in their Lightbox Collection. The prices of these stones are competitive, too. With their customer service, James Allen is an excellent choice when looking for a lab-grown diamond. Buying a ring from them is also a great way to support the local community by supporting rainforest conservation initiatives.
The process used to create a lab-grown diamond is known as “CVD” or chemically induced. The IGI grades these gems on a D-Z scale. A D colored diamond has no visible tint, while a Z-graded diamond has a noticeable yellow or brown tint. Inclusions in a lab-grown diamond do not always appear visible to the naked eye, but they are usually present.
In this method, the diamond is created inside a laboratory by placing a carbon seed in a chamber similar to the natural environment of diamond formation. This carbon seed is then exposed to high temperatures and pressures, and the final product is a man-made diamond. Because lab-grown diamonds have the same properties as natural diamonds, only high-tech equipment can distinguish them from each other.
A lab-grown diamond’s beauty and price can vary considerably from its video image. The video may be low-quality due to low exposure, or it may have light leakage. In addition, the clarity scale of a CVD pear-shaped lab-grown diamond is similar to a natural diamond’s. While a lab-grown diamond will test as a diamond, it’s unlikely to produce the same level of quality.
When selecting a lab-grown diamond, remember to choose one that has been certified by an independent third-party laboratory. While lab-grown diamonds are synthetic, they are still graded according to the 4Cs, and IGI has embraced their quality standards. However, before choosing a lab-grown diamond, consider your budget and the cut that you prefer. You’ll also need to take a look at the diamond’s clarity, color, and cut.
CVD Pear Shaped Lab Created Diamond FGH VS